The recent apartment block fire in Vietnam ignited rumors suggesting it was caused by an electric bike battery. However, upon investigation by the authorities, it was confirmed that a gasoline bike was the culprit. This raises the question: Are electric vehicles or gasoline vehicles more prone to causing fires? Thanks to cutting-edge battery manufacturing technology, lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles are generally considered safe.

The advanced technology in electric vehicle batteries, particularly the advances achieved in making them fire-resistant, is a crucial aspect of this revolution. This innovation addresses one of the main issues with lithium-ion batteries, making EVs safer as well as more environmentally beneficial.
Advanced battery management systems
The creation of cutting-edge Battery Management Systems (BMS) is one of the main factors contributing to the improved safety of the batteries used in electric vehicles. These devices are essential for managing and keeping track of the battery’s condition. A variety of sensors and algorithms are used by modern BMS to keep the battery functioning within safe limits.
The battery’s temperature is regularly monitored by temperature sensors to ensure it stays within safe bounds. If the temperature begins to increase significantly, the BMS can intervene to prevent overheating by lowering the charging rate or even momentarily turning off the battery.
Battery voltage levels are monitored via voltage sensors, which can flag potential issues. If the voltage becomes unstable or exceeds acceptable limits, the BMS intervenes to ensure safety.
Cell balancing
Another vital component of battery management is cell balancing. Individual cells in a typical lithium-ion battery pack might differ slightly in their capacity and properties. These variations can cause uneven charging and discharging over time, which might increase the risk of overheating and fires.
To keep all the cells in a battery pack balanced, modern BMS systems employ cell-balancing procedures. This helps maintain consistent performance across all cells, reducing the possibility of an unstable or overheated cell.
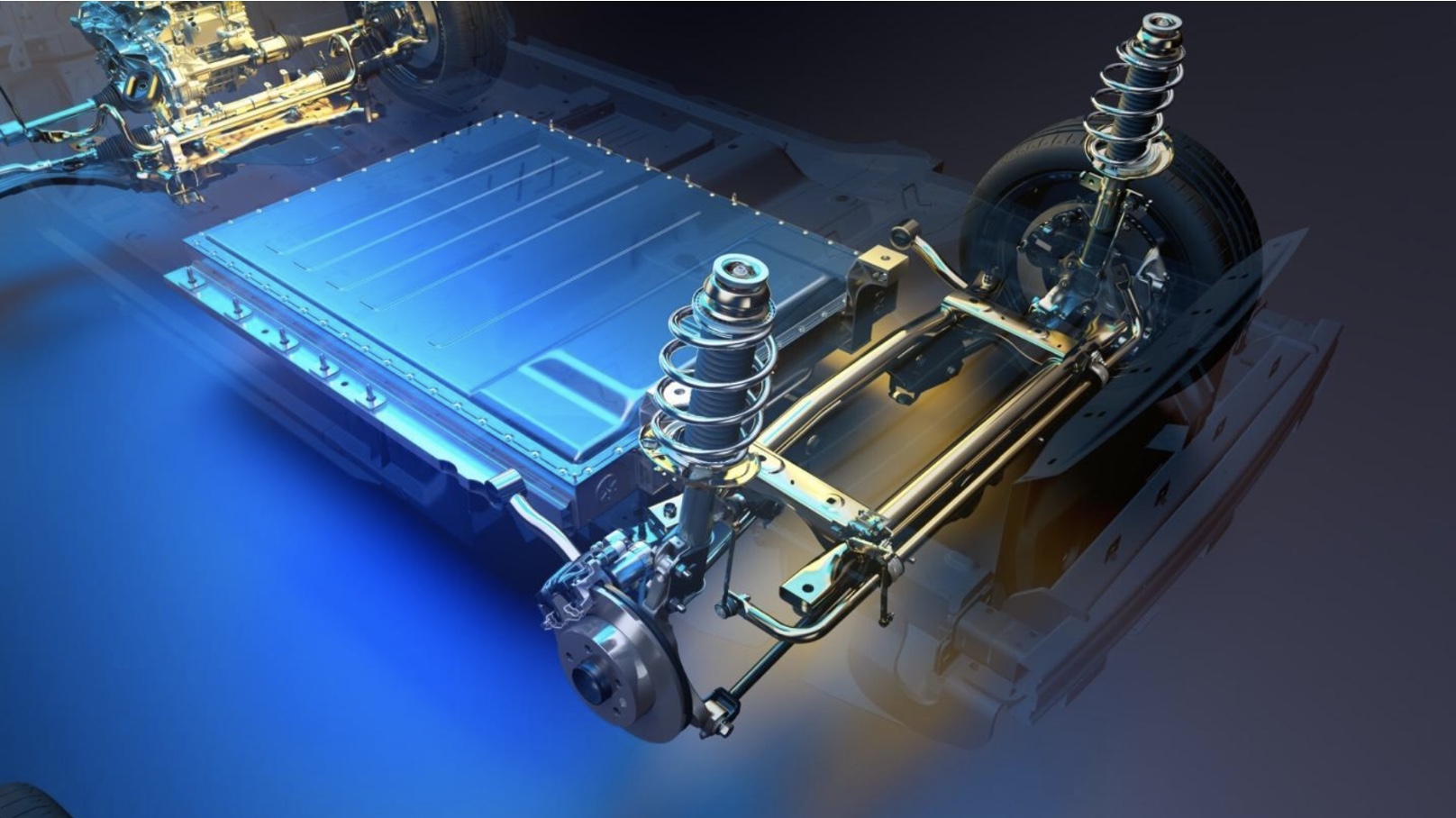
Enhanced thermal management
In order to prevent battery overheating, proper thermal management is essential. Manufacturers of electric vehicles have been investing in cutting-edge thermal management technologies to keep their batteries cool under a variety of circumstances.
In many EVs, liquid cooling systems are standard. These systems dissipate the heat generated during charging and discharging using a network of coolant-filled channels. Some EVs even include active cooling, where fans or pumps help to more efficiently control the temperature.
Unlike conventional petrol-powered vehicles, EVs have sophisticated temperature management systems, safe battery enclosures, and strict safety regulations. These features greatly reduce the risk of fires, particularly in underground garages.

Innovative materials
To enhance safety, the materials used in battery manufacturing have also evolved. Researchers are investigating alternative electrode materials that are more stable at high temperatures and less susceptible to thermal runaway.
For instance, silicon anodes are being explored as an alternative to traditional graphite anodes. While silicon has historically experienced significant expansion and contraction during charge and discharge cycles, leading to battery degradation and associated safety concerns, it can store more energy. Modern engineering techniques and materials have been developed to address these challenges.
Contingency measures
In addition to proactive safety features, electric vehicle manufacturers are incorporating contingency measures to reduce the risk of battery fires. These measures include fire-resistant enclosures for battery packs and dedicated safety systems that can isolate a damaged or overheating cell to prevent further escalation.
In the event of a collision or external damage, sensors and safety systems can swiftly disconnect the affected part of the battery, isolating it from the rest of the pack to avert a catastrophic failure. This not only safeguards occupants but also minimizes the risk of fires spreading.
Stringent testing and regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies have established rigorous testing and certification systems to ensure the safety of electric car batteries. Electric vehicle manufacturers must comply with specific standards to sell their vehicles in various regions. These standards encompass a wide range of aspects, from battery performance and safety to durability.
For instance, the United Nations Global Technical Regulation on Electric Vehicle Safety sets comprehensive safety criteria for electric vehicles, including battery safety. Complying with such regulations ensures that EVs meet rigorous safety standards, reducing the likelihood of battery-related incidents.
The development of electric car battery technology has always prioritized safety, especially in minimizing the risk of fires. Every facet of EV battery design and technology has evolved to make these vehicles safer on the road, from enhanced battery chemistry and superior thermal management systems to advanced battery enclosures.
Though electric car battery fires remain rare, the continuous enhancement of safety systems and strict regulatory standards build public confidence in EVs. As electric vehicles gain traction in the automotive industry, these advancements will play a pivotal role in accelerating their acceptance and ensuring safer roads for all. The future of electric vehicle battery technology involves more than just extending range and improving efficiency.
Installing charging stations for electric vehicles is intrinsically linked to safety. Owing to the aforementioned safety technologies, many high-rise buildings, be it offices or apartments, have now adopted policies to allocate areas for electric vehicle charging. For instance, the Japanese government plans to ease regulations on the construction of fast-charging electric car charging stations to bolster Japan’s EV charging infrastructure. The goal is to establish 150,000 charging stations across the nation by 2030, of which 30,000 will be fast-charging stations.
Will Davis is a freelance writer covering economic, automobile, and lifestyle topics in Vietnam.
TNGlobal INSIDER publishes contributions relevant to entrepreneurship and innovation. You may submit your own original or published contributions subject to editorial discretion.

